SiC membrane-based FZP, only from NTT-AT in the world
Benefits
NTT-AT's Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP), constructed from SiC membrane and Ta absorber pattern, has an outstandingly high X-ray irradiation durability, high resolution, and high contrast.Only NTT-AT provides the SiC membrane-based Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP), which has an outstandingly high X-ray irradiation durability. NTT-AT's FZP is constructed from dry etched Ta. It has a sharp absorber pattern and achieves a high S/N ratio and low defect imaging, and is ideal for applications such as X-ray microscopes, X-ray micro-beam irradiation, and X-ray imaging.
In addition, the Ta pattern/SiN membrane-type FZP and Au plated pattern/SiN membrane-type FZP are provided for using in soft X-ray and extreme ultraviolet (EUV/XUV) regions. In addition, a Step (Kinoform) FZP is available.
Features
Key points
- Useful for various X-ray applications such as X-ray microscopes, EUV microscopes, X-ray microbeam irradiation, and synchrotron radiation beam monitors, etc.
- Outstandingly high X-ray irradiation durability
- Minimum zone width up to 25 nm
- Customized FZP also available
Standard product list with specifications
| Model | Aspect Ratio | Membrane Material | Membrane Thickness (µm) | ΔRn (nm) | D (um) | N | Tm (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FZP-S38/84 | 4.2 | SiN | 0.15 | 38 | 84 | 550 | 160 |
| FZP-S50/80 | 5 | SiN | 0.2 | 50 | 80 | 400 | 250 |
| FZP-S40/155 | 5 | SiN | 2 | 40 | 155 | 970 | 200 |
| FZP-S50/330 | 8 | SiN | 1 | 50 | 330 | 1,650 | 400 |
| FZP-S86/416 | 8 | SiN | 2 | 86 | 416 | 1,200 | 700 |
| FZP-100/155 | 8 | SiN | 2 | 100 | 155 | 388 | 800 |
| FZP-173/208 | 5.8 | SiN | 2 | 173 | 208 | 300 | 1,000 |
| FZP-200/206 | 8 | SiN | 2 | 200 | 206 | 255 | 1,600 |
| FZP-C234/2500 | 0.6 | SiC | 0.2 | 234 | 2,500 | 2,670 | 150 |
Rn : Outermost Zone Width
D : Diameter
N : Total Zone
Tm : Ta Thickness
Standard lead time: 12 weeks
X-ray absorber pattern of Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP)
Custom designed FZPs are available upon request to suit your specific X-ray energy, optical setup and focus/image performance. Please feel free to contact us if you cannot find a product that meets your requirements in our catalogue of standard products. Pattern image (φ2.5mm)
Pattern image (φ2.5mm)(Optical microscope)
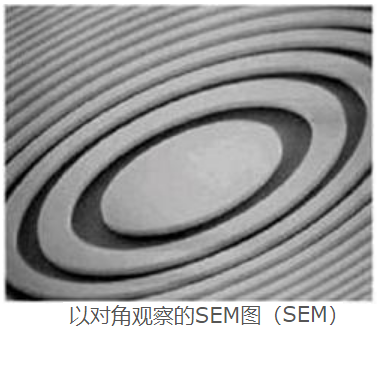
 Observed SEM image with diagonal angle
Observed SEM image with diagonal angle(SEM)
Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) Structure
 Binary type
Binary type Step (kinoform) type
Step (kinoform) type| Minimum zone width (outer most zone) | 25nm |
|---|---|
| Maximum diameter | 5mm |
| Membrane material | SiN, SiC |
| Membrane thickness | 0.2-2µm |
| Absorber material | Ta |
| Absorber thickness | 0.1-2µm |
| Si substrate shape | 10mm square |
| Si substrate thickness | 1mm |
X-ray Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) Inquiry
Production example
Ultra fine pattern Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP)
Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) diameter : 250µm, Ta thickness : 125nm, Outermost zone width : 25nm, Membrane : SiC 2.0µm

High aspect ratio (thicker Ta absorber) Fresnel Zone Plate(FZP)
Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) diameter : 100µm, Ta thickness : 2.5µm, Outermost zone width : 250nm, Membrane : SiN 2.0µm

Step (Kinoform) type Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP)
Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) diameter : 100µm, Ta thickness : 4.0µm, Outermost zone width : 400nm, Membrane : SiC 2.0µm

X-ray Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) Inquiry
Past record
The FZP with a combination of high durability, SiC membrane and sharp-shaped Ta X-ray absorber results in a tough and highly accurately shaped product.NTT-AT's FZP has been used in many products throughout the world, proving of its high quality.
Paper lists
- Nobuhito Nango, Shogo Kubota, Akihisa Takeuchi, Yoshio Suzuki, Wataru Yashiro, Atsushi Momose, and Koichi Matsuo, “Talbot-defocus multiscan tomography using the synchrotron X-ray microscope to study the lacuno-canalicular network in mouse bone,” Biomed. Opt. Express 4, 917 (2013); http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/BOE.4.000917
- K. Nogita, H. Yasuda, M. Yoshiya, S.D. McDonald, K. Uesugi, A. Takeuchi, and Y. Suzuki, “The role of trace element segregation in the eutectic modification of hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys,” J. Alloy Compd. 489, 415 (2010); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.09.138
- Yasushi Kagoshima, Hidekazu Takano, Takahisa Koyama, Yoshiyuki Tsusaka and Akihiko Saikubo, “Tandem-Phase Zone-Plate Optics for High-Energy X-ray Focusing,” Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 50 022503 (2012); http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.50.022503
- extreme-ultraviolet scatterometry microscope
Tetsuo Harada, Yusuke Tanaka, Takeo Watanabe, Hiroo Kinoshita, Youichi Usui and Tsuyoshi Amano, “Phase defect characterization on an extreme-ultraviolet blank mask using microcoherent,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 31, 06F605 (2013);http://dx.doi.org/10.1116/1.4826249 - Nobuhiro Yasuda, Yoshimitsu Fukuyama, Shigeru Kimura, Kiminori Ito, Yoshihito Tanaka, Hitoshi Osawa, Toshiyuki Matsunaga, Rie Kojima, Kazuya Hisada, Akio Tsuchino, Masahiro Birukawa, Noboru Yamada, Koji Sekiguchi, Kazuhiko Fujiie, Osamu Kawakubo and Masaki Takata, “System of laser pump and synchrotron radiation probe microdiffraction to investigate optical recording process,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84, 063902 (2013); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4807858
- Yoshio Suzuki and Akihisa Takeuchi, “X-ray holographic microscopy with Fresnel zone plate objective lens and double-diamond-prism interferometer,” Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 53 122501 (2014); http://dx.doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.53.122501
- Masanori Tomitaa , Munetoshi Maeda, Katsumi Kobayashi and Hideki Matsumoto, “Dose Response of Soft X-Ray-Induced Bystander Cell Killing Affected by p53 Status,” Radiation Res. 179, 200 (2013); http://dx.doi.org/10.1667/RR3010.1
- W. Yashiro, Y. Takeda, A. Takeuchi, Y. Suzuki, and A. Momose, “Hard-X-Ray Phase-Difference Microscopy Using a Fresnel Zone Plate and a Transmission Grating,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 180801 (2009); http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.180801
- Yutaka Yoshida , Kazuo Hayakawa, Kenichi Yukihira, Masahiro Ichino, Yuki Akiyama, Hiroto Kumabe, Hiroyoshi Soejima, “Development and applications of “Mössbauer cameras”,” Hyperfine Interact. 198, 23 (2010); http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10751-010-0228-x
- Akihisa Takeuchi, Yasuko Terada, Kentaro Uesugi, Yoshio Suzuki, “Three-dimensional X-ray fluorescence imaging with confocal full-field X-ray microscope,” Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. A 616, 261 (2010); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2009.10.054
- K. Horiba, Y. Nakamura, N. Nagamura, S. Toyoda, H. Kumigashira, M. Oshima, K. Amemiya, Y. Senba and H. Ohashi, “Scanning photoelectron microscope for nanoscale three-dimensional spatial-resolved electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 113701 (2011); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3657156
- Tatsuya Kikuzuki, Yuya Shinohara, Yoshinobu Nozue, Kazuki Ito, Yoshiyuki Amemiya, “Determination of lamellar twisting manner in a banded spherulite with scanning microbeam X-ray scattering,” Polymer 51, 1632 (2010); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.01.057
- Sho Kanzaki, Yasunari Takada, Shumpei Niida, Yoshihiro Takeda, Nobuyuki Udagawa, Kaoru Ogawa, Nobuhito Nango, Atsushi Momose, Koichi Matsuocorrespondenceemail, “Impaired Vibration of Auditory Ossicles in Osteopetrotic Mice,” Am. J. Pathol. 178, 1270 (2011); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.063
- Akihisa Takeuchi, Kentaro Uesugi and Yoshio Suzuki, “Three-dimensional phase-contrast X-ray microtomography with scanning–imaging X-ray microscope optics,” J. Synchrotron Rad. 20, 793 (2013); http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0909049513018876
- Akihisa Takeuchi, Yoshio Suzuki and Kentaro Uesugi, “Differential phase contrast X-ray microimaging with scanning-imaging x-ray microscope optics,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83, 083701 (2012); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4739761
Publication list (including co-authored papers):
- Akihisa Takeuchi, Yoshio Suzuki, Kentaro Uesugi, Ikuo Okada and Hiroki Iriguchi, “Performance Test and Evaluation of Multilevel Fresnel Zone Plate with Three-Step Profile Fabricated with Electron-Beam Lithography,” Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 51 022502 (2012); http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.51.022502